Prices of new petrol and diesel cars on the rise – electric vehicles less affected
30 May 2022

As inflation continues to rise in Europe, Christof Engelskirchen, chief economist of Autovista Group, explores why carmakers are pushing up the price of internal-combustion engine (ICE) vehicles more than electric vehicles.
Eurozone inflation is rising, with the latest consensus suggesting it will sit around 7% for 2022 in the European Union and the UK. This rise has been spreading into the automotive sector, underpinned by ongoing supply shortages of new and used cars. Price rises are being further compounded by a steep ascent of raw-material and energy costs as a result of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Autovista24 expects the trend of rising new-car prices to continue as long as supply constraints remain ubiquitous. This will positively affect used-car prices as well – if demand cannot be met on new-car markets, buyers will turn to used models and this supports price realisation. Carmakers will have no other choice than to increase prices to support their margins.
Not all vehicle powertrains are affected in the same way, however. Prices for ICE models have been rising more than those of electric vehicles (EVs) over the past year. There are substantial segment differences too, as can be witnessed in the German market.
Gross list-price changes by segment in Germany – April 2022 year on year
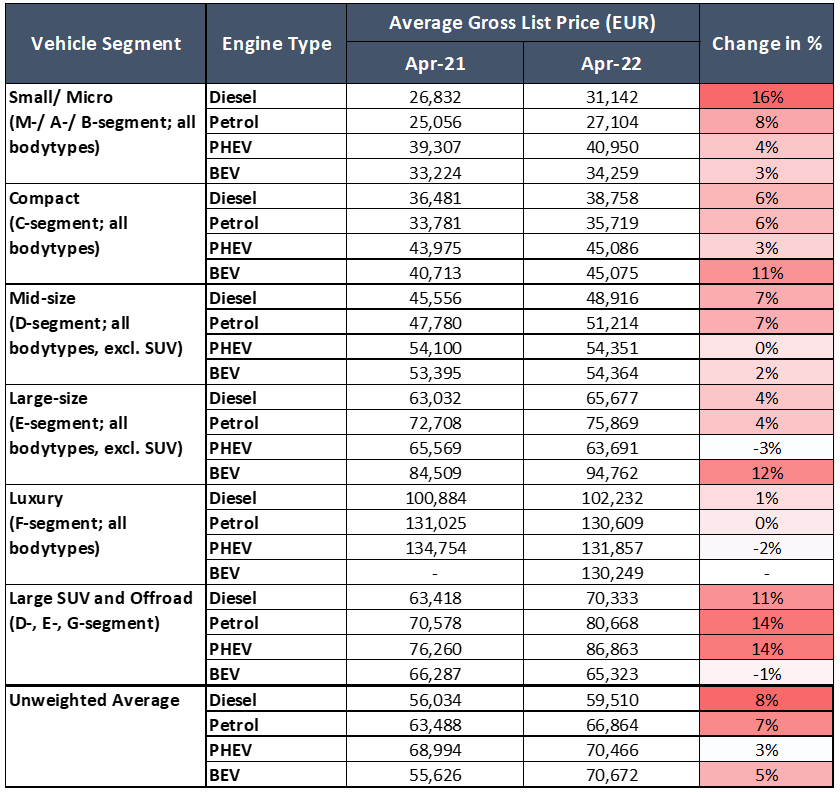
Prices for diesel and petrol vehicles rise on a similar scale within the same segment. For example, in the mid-size segment (e.g. BMW 3-Series, Audi A4 and Mercedes-Benz C-Class), both powertrain types have risen by 7% over the past year. In the large-vehicle segment, prices for each rose by 4%, while in the compact-vehicle segment petrol and diesel-vehicle prices rose by 6%. This was no coincidence. In fact, they appear to be equally affected by rising costs of materials and are treated similarly from a carmaker’s pricing-strategy perspective.
There was one exception to the parity in this development. Diesel prices in the small-vehicle segment (e.g. Opel/Vauxhall Corsa, Volkswagen Polo and Renault Clio) have jumped on average by 16%, which has been driven by the added costs to emissions treatment, which weigh more heavily on cars in this segment. Petrol-vehicle prices only rose by 8%.
Steering customers towards electric powertrains
OEMs are shifting their portfolios towards battery electric vehicle (BEV) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs). It is no surprise, therefore, that price rises for BEVs were more moderate than those of petrol and diesel vehicles: 3% in the small-vehicle segment and 2% in the mid-size segment.
In the compact-vehicle segment, the average price rise of 11% for BEVs can be attributed to the launch of the Hyundai Ioniq 5, which changed the mix and drove average prices up. Similarly, the 12% increase in the large-size segment was driven by the Taycan Cross Turismo debuting in May 2021.
PHEV price rises are also substantially more moderate than for ICE vehicles, given their contribution to meet EU CO2-emissions standards. The exception was a 14% price increase in one year in the large-SUV segment, which was driven by price increases from BMW. Overall, the number of PHEV-powertrain offerings was still relatively small, so every new launch affects vehicle-price averages significantly.
While price rises for BEVs and PHEVs have been more moderate, the prices of ICE vehicles are almost exactly trailing annual inflation rates (around 7% to 8%). Higher price rises for ICE vehicles than for BEVs and PHEVs are evidence that most carmakers are steering customers towards electric powertrains.
Higher inflation in eastern-European countries
Annual inflation stayed at a high level in April 2022, driven by price rises for food and energy. April’s Eurozone annual inflation remained stable at a high 7.4%, while inflation in the UK was 7%. Prices have been rising since the beginning of 2021, but it is worth noting that the Ukraine war has driven energy and food prices through the roof. If you take these out of the equation, annual inflation would have been around 3.5% in April.
Inflation was much higher in eastern than in western-European countries. For example, in the Czech Republic, annual inflation rose to 14.2% in April. In Estonia it was 18.9%, Lithuania 16.8%, and Poland 12.4%.
Spain was one of the few countries where inflation fell in April, to 8.3% from 9.8% in March. Countries that are less dependent on energy (and food) imports, like Spain, show lower inflationary tendencies. Other examples include Norway at 5.4%, and France at 4.8% in April.
Inflation outlook above 6% in Europe
Inflation is expected to surge to around 7% in both the EU and the Eurozone for the full year of 2022, with some central and eastern-European countries likely to see double-digit price rises in this timeframe. For 2023, the EU’s inflation will likely fall to 2.7%, but still sit above the European Central Bank’s (ECB’s) 2% target. Interest-rate rises in July are very likely in the Eurozone.
It is worth noting that the next possible escalation of the Ukraine war could result in a stoppage of oil and gas supply from Russia, which would trigger a gloomier scenario. The EU expects gross domestic product (GDP) growth to come down from an already subdued 2.5% in 2022 to 0.2%, and inflation would be 3% higher than in the base case, perhaps approaching 10% in that scenario this year. In 2023, inflation would be one point higher than in the base case, i.e. around 4%.
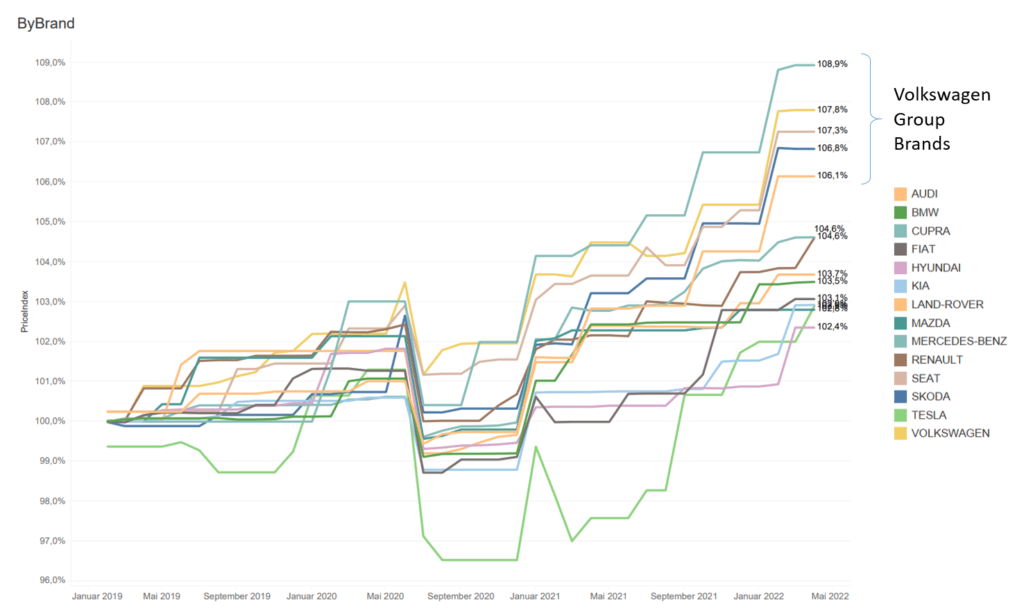
Volkswagen Group prices higher than others
Across all powertrain types, and controlling for changes in the model mix, Volkswagen (VW) Group brands led the way in terms of price rises. Audi, Cupra, Seat, Skoda and VW have increased prices more than other carmakers (see chart below). There are two possible reasons for this:
- They are pushing customers towards electric powertrain types, via price rises for ICE vehicles
- They are particularly affected by supply constraints, which leads the brands to consolidate their margins via price rises more than other OEMs.
New-vehicle price index in Germany by brand January 2019 to April 2022
(graphic opens in new tab)
In terms of price development, Kia and Hyundai are at a comparably low 102.9% and 102.4% level respectively. They are apparently less exposed to supply issues than VW Group brands and are building market share with their more moderate pricing strategy. According to Germany’s national ministry of vehicle transport, the KBA, Kia’s market share in the country in April 2022 was 3.8%, compared to 2.4% in April 2021. Hyundai grew its April market share from 3.3% to 4.1%. VW, on the other hand, dropped from an 18.8% market share in April 2021 to 16.6% in the same timeframe.



