Carmakers successfully pooled emissions to meet 2020 EU targets
20 May 2021

Autovista Group senior data journalist Neil King investigates the emissions performance of major carmakers in the EU in 2020. In this first part, King discusses pooling and focuses on manufacturers that successfully spread their emissions over a larger fleet average.
The issue of CO2 targets has given many carmakers a headache in recent years. Until 2016, many relied on diesel engines to help them achieve their goals. Yet, the collapse in trust and sales of this technology left manufacturers scrambling for alternatives, especially as consumers switched to the higher CO2-emitting petrol cars and SUVs. The best option was to push ahead with plans for both hybrid and electrically-chargeable vehicles (EVs).
Some carmakers were more advanced in developing these technologies, which led to several manufacturers combining their fleets into pools, spreading out CO2-emission figures over a larger area and reducing the chances of a fine.
Manufacturers established a number of pools to help meet their 2020 and 2021 targets, and all but one was successful last year. Volkswagen Group, part of the biggest pool by market share, missed its projection by a small margin, just 0.5g. However, every carmaker managed to reduce their average fleet emissions, compared to 2019.
Running the numbers
From 2021, the average emissions target for new cars registered in the EU is set at 95g/km CO2. For every 1g/km of CO2 a manufacturer exceeds its average emissions target by, it is fined €95, multiplied by its volume of new-car registrations in the preceding year. However, the highest-polluting 5% of new cars registered in 2020 are excluded from the 2021 fines calculations, which serves as a transitional phase for carmakers.
Based on analysis of data distribution, Autovista Group calculates that this reduced average CO2-emissions figures by about 7%. From 2022 onwards, however, full compliance of all new cars is required (i.e. new cars registered in 2021 onwards).
Pool party
The idea of a pool is simple. A carmaker struggling to meet targets reaches out for help to those who are more successfully managing their CO2 output. Once in the pool, both sets of emissions figures are combined and spread out over an expanded fleet, reducing the average and, in most cases, helping the struggling company achieve its target and avoid a fine. The compliant manufacturer will likely receive financial compensation for its help.
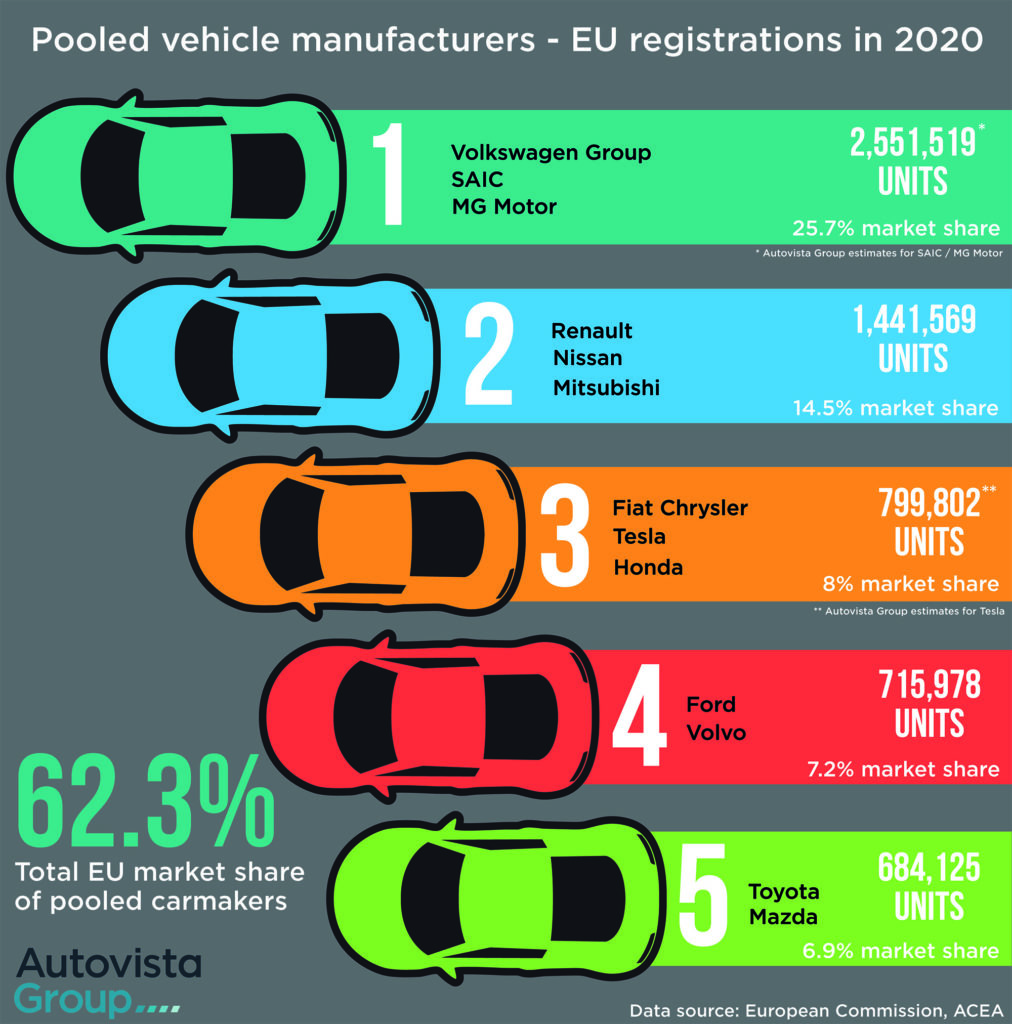
Of all the major manufacturers in Europe, Toyota was in the strongest position to meet its emissions target in 2020. Compared to their 2017 level, the Japanese group only had to reduce their average fleet emissions by 9g CO2/km (9%).
The manufacturer has not revealed detailed emissions figures but has confirmed it met its target, supported by strong demand for its hybrid-electric vehicles.
Therefore, the OEM was able to help fellow Japanese manufacturer Mazda, which only launched its first BEV, the MX-30, in 2020. Similarly, Renault, Nissan and Mitsubishi pooled their emissions. The Renault Group itself benefitted from the Zoe BEV and its extended range of E-Tech hybrid and plug-in hybrid (PHEV) variants of models such as the Clio, Captur and Megane.
Nissan’s fleet-average emissions were aided by the Leaf BEV and, combined, Renault-Nissan was only 2g/km short of its target in the first half of 2020. In order to comply with European emissions targets going forward, Mitsubishi Motors will source models from Renault that meet regulatory requirements. ′Starting 2023, Mitsubishi Motors will sell two ″sister models″ produced in Groupe Renault plants, which are based on the same platforms but with differentiations, reflecting the Mitsubishi brand’s DNA,’ Renault revealed.
Recall issues
As an example of the fine lines that manufacturers walk to meet their emissions targets, Ford was forced to consider pooling towards the end of 2020. The carmaker issued a recall of its Kuga plug-in hybrid (PHEV) in August of last year. As the carmaker did not have a battery-electric vehicle (BEV) in its fleet, it was heavily reliant on the PHEV to lower CO2 levels.
Ford had already faced a higher mountain to climb, with its 2017 emissions figures showing it needed to reduce CO2 output across its fleet by 26g/km (21%). The recall led the manufacturer to announce it was considering pooling, in order to meet its targets.
′The current issues with the Kuga PHEV, resulting in a stop-ship and stop-sale have affected our plan to meet the EU’s 2020 emissions regulations for passenger vehicles on our own,’ Ford said to Autovista Group at the time. ′Therefore, just as many other OEMs have done in Europe, we now intend to join an open pool with other OEMs for passenger vehicles.’
Ford entered into an agreement with Volvo in November. Although the US carmaker has not provided detailed figures, it did meet its 2020 target, likely thanks to this pool.
Sought after
Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA) faced the biggest challenge to comply with European emissions targets.
The US-Italian group needed to lower their emissions by 29g/km (24%) compared to 2017 levels. This largely explains why FCA pooled its emissions figures with US BEV manufacturer Tesla. The move brought FCA’s average CO2 emissions down by offsetting the company’s petrol and diesel vehicles from Fiat, Jeep, Alfa Romeo and Maserati against the zero-emission outputs of Tesla’s BEVs.
CEO Mike Manley already suggested in August 2019 that the Italian carmaker would be compliant because of the regulatory credit deal with Tesla. Honda was subsequently brought into this pool too.
Tesla is the largest BEV-only carmaker in Europe, having entered the market in 2008 with its limited production Roadster, before launching its first BEV sedan, the Model S, in 2012. The manufacturer built up a base of BEV models while other carmakers continued to promote ICE and was well-placed to capitalise when consumers started considering alternative options.
Therefore, its CO2 credits would provide a good opportunity for carmakers to reduce their overall levels. While the US company sells fewer vehicles than bigger players in the automotive market, average emissions across its entire fleet will be no higher than zero.
The FCA annual report states that CO2 emissions data for last year is not yet available but: ′the 2020 result is expected to move toward the 95g CO2/km EU average target due to the adoption of a multi-faceted approach which leveraged conventional technologies, high-voltage electrification, pooling arrangement contribution and compliance rules for 2020.’
′The quantity of CO2 emissions in 2021 will be affected not only by market evolution (such as the expected reduction of diesel market share) but also by the commercialisation of low-emission and electrified vehicles. Finally, according to applicable EU regulations, current pooling arrangements for emissions compliance for passenger cars entered into by FCA are expected to apply in 2021,’ FCA added.
However, at the start of 2021, FCA merged with PSA Group to form Stellantis. CEO of the new manufacturing group, Carlos Tavares, has since been reported to have terminated the agreement with Tesla. As PSA Group met its emission targets in 2020, and as FCA’s figures will now merge with these, the company should be in a position to achieve its CO2 goals at the end of this year.
In the next instalments of this series, Neil King will explore those manufacturers who met their emissions targets on their own and carmakers who failed to reduce CO2 sufficiently, whether they pooled or not.